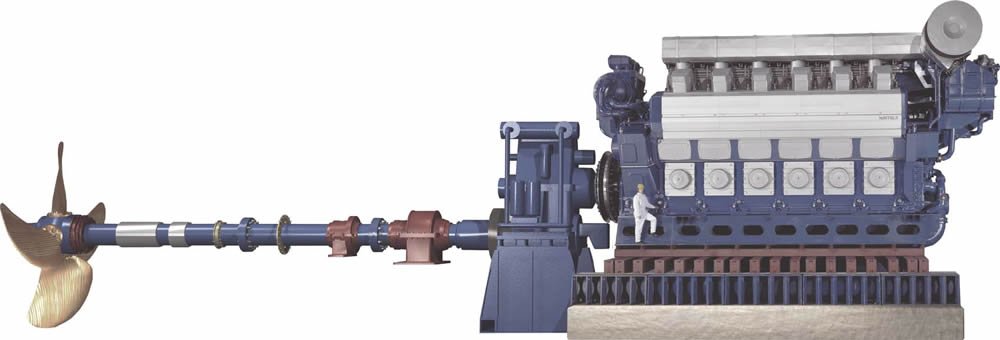
A diesel engine power plant is a viable and reliable source of power. It operates based on a diesel engine, which converts the chemical energy stored in fuel into mechanical work, which results in an alternator producing electrical energy. This article illustrates how a diesel engine works in an engine-based power plant.
Fuel Injection System: The engine’s fuel injection mechanism is required functionality in a diesel engine power plant. In general, it is necessary to introduce a specific amount of diesel fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber during the proper time frame. The system comprises a fuel pump, fuel injectors, and fuel injection lines. The fuel pump is charged with pressuring diesel fuel, while the fuel injectors dispense calculated heights of the fuel into the combustion chamber as a cloudy mixture to ensure efficiency-driven combustion.
Air Intake System: Intake of the air system is important to guarantee that the combustion chamber receives clean, filtered, and non-toxic air during the combustion process. The cooled air enters the air intake system through an air filter before being compressed with a turbocharger or a supercharger; pre-dry bulb cooler L. The diesel engine power plant is governed by the compression ignition rule. After the air is compressed and cooled, the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber. The high pressure and temperature of air inflow spark self-ignite diesel fuel without the need for a spark plug. This process produces a large volume of energy that flows into engine-mechanical-energy.
Power Generation: The mechanical energy converted from the chemical energy of the fuel by the diesel engine is utilized to drive an alternator. The latter is a generator that transforms the mechanical energy into electrical energy. It is composed of a moving magnetic field and a stationary coil. Movement of the engine revolves the magnetic field which causes the coil to generate an electric current by induction. The current produced powers the entire plant.
Cooling System: A cooling system is essential in a diesel engine power plant to regulate and maintain optimum temperatures. The cooling system involves the circulation of coolant, water mixed with antifreeze, circulating to the engine to absorb heat. The coolant is then pumped to a radiator, where it is cooled and then recirculated back to the engine.
Exhaust System: The exhaust system in a diesel engine power plant is responsible for the elimination of combustion gases from the engine area. It consists of an exhaust manifold that collects the combustion gases from cylinders to pipes and mufflers which drive the gases out of the plant. The gas is first passed through a catalytic converter, which eliminates a substantial component before IT is released into the atmosphere.

Lubrication System: It is a system used to reduce friction between moving components and extend engine service life. It involves enveloping moving components with oil.
Control System: A control system also regulates the operation and monitors various other parameters of the diesel engine power plant. It is equipped with sensors and controllers to take measurements of engine speed, engine temperature, pressure, and fuel flow. Based on these inputs, the control system readjusts the fuel injection timing, the air intake, and other operations essential to optimize performance and efficiency.
Maintenance and Safety: Maintenance and safety measures play a vital role in ensuring that the diesel engine power plant operates efficiently and safely. Maintenance includes regular servicing, such as oil changes, filter replacements, and inspections to prevent unexpected breakdowns. The diesel engine power plant is also equipped with fire prevention systems, emergency shutdown procedures, and ventilation to protect both personnel and assets from hazards and accidents.

Fuel Supply System: The fuel supply system in the diesel engine power plant handles the storage, filtering, and supply of fuel to the engine . The system comprises diesel fuel storage tanks, fuel filters, and fuel pumps connecting the storage to the engine. The fuel is injected under pressure into the combustion chamber, where it mixes with air before combustion. Power Generation: The engine is the core of the diesel engine power plant that converts the chemical energy of fuel into mechanical energy. The mechanical energy is used to run a generator that converts it into electrical energy. The generator is connected to several electrical circuits, through which it powers the plant, machinery, or any other electrical load.
Load Management Diesel engine power plant is expected to be able to operate under all loads. Load management systems make certain that the load is proportional to or less than what the generator can produce to avoid overloading the system. They constantly watch the electrical loads and adapt the fuel supply and engine speed to ensure a stable and balanced power supply.
Backup Power Because of its utilization as an emergency or backup generating plant to generate electricity throughout disturbances in the grid supply or fuel system, the diesel engine power plant plays a vital role. Systems that are essential and must be supplied with electricity to operate properly and remain in action throughout an accident in which the main power source is shut down or unable to power the plant can be a lifesaver.
Exhaust System Apart from water, almost all diesel engines produce at least some exhaust. The exhaust system is essential in removing the combustion by-products as well as reducing available emissions. The exhaust gases must be treated before being sent out the stack or conveyed into the air to make them less damaging to the environment.
Waste Heat Recovery Most power plants burn fuel to create heat electricity. A diesel engine power plant is a type of power plant that generates heat as it works. The heat that cannot be converted into power at the plant is transported to the atmosphere; producing steam.
Noise Control Since a diesel power plant is a noisy location, soundproof constructions that enclose the equipment are often used. These enclosures reduce the transmission of sound waves and create a noiseless work atmosphere.
Emissions Control As the issue of the environment becomes more and more important, diesel engine power plants use various emissions control mechanisms. Their goal is to reduce the extent to which the operation of the plant impacts air quality, while also seeking to reduce the number of harmful substances released by the plant into the atmosphere. The key unit in emissions control in a diesel engine power plant is the catalytic converter . This device helps to transform the most harmful pollutants, including nitrogen oxides and carbon monoxide, into somewhat less harmful substances before they enter the atmosphere. Catalytic converters are built with catalysts in them, although contact with these substances leads to chemical reactions in which they disintegrate and transform.