Introduction
A Comprehensive Study of Vacuum Circuit Breaker
Vacuum circuit breakers (VCBs) play a crucial role in modern electrical systems, ensuring the safe and efficient interruption of electrical circuits. They are renowned for their reliability, longevity, and minimal maintenance requirements. This article delves into the workings, advantages, types, and applications of VCBs, providing a thorough understanding for both novices and experts in the field.
What is a Vacuum Circuit Breaker?
Understanding Vacuum Circuit Breakers
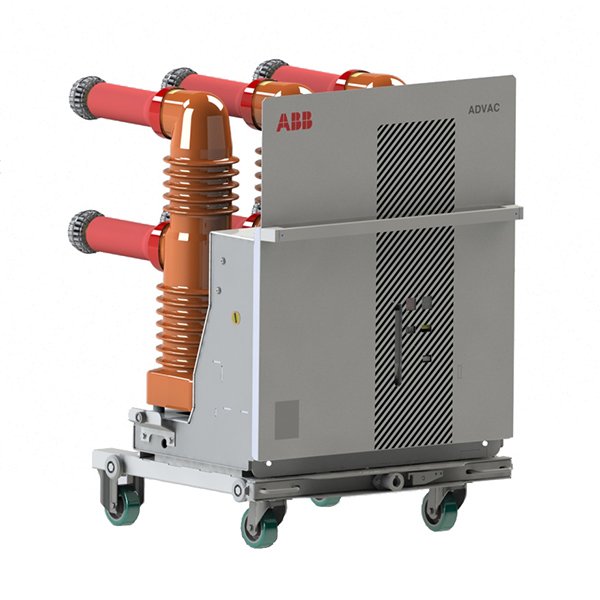
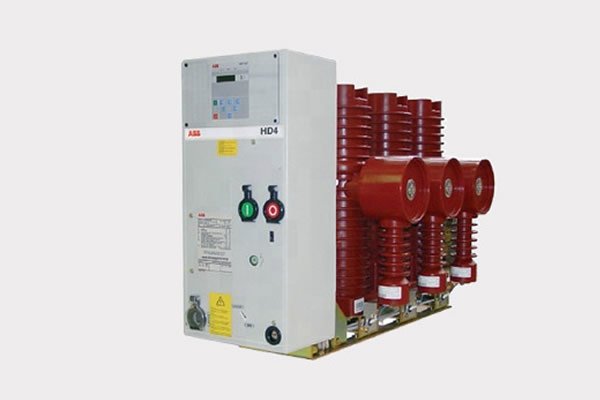
A vacuum circuit breaker (VCB) is a type of circuit breaker where the arc quenching takes place in a vacuum environment. Unlike other circuit breakers that use oil, gas, or air to extinguish the arc, VCBs rely on the vacuum, which is a superior medium for arc extinction due to its high dielectric strength.
Historical Development: The development of vacuum circuit breakers began in the early 20th century. They gained prominence in the 1960s as technology advanced, making them more efficient and reliable. Over time, VCBs have become a staple in industrial, commercial, and residential electrical systems due to their durability and environmental benefits.
How Does a Vacuum Circuit Breaker Work?
Mechanism of Vacuum Circuit Breaker
The Principle of Arc Quenching in Vacuum
When a circuit breaker operates, it opens the circuit, creating an arc between the contacts. In VCBs, this arc is extinguished in a vacuum chamber. The vacuum has an excellent insulating property and a high dielectric strength, which effectively quenches the arc quickly. The absence of gas or oil eliminates the risk of fire or explosion, making VCBs safer.
Components of a Vacuum Circuit Breaker
VCBs consist of several key components:
- Vacuum Interrupter: This is the core component where the arc quenching happens. It contains the fixed and moving contacts in a sealed vacuum container.
- Contacts: These are made of materials that withstand high temperatures and arc energy, ensuring minimal wear and tear.
- Operating Mechanism: This mechanism controls the movement of the contacts, enabling the opening and closing of the circuit.
Types of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
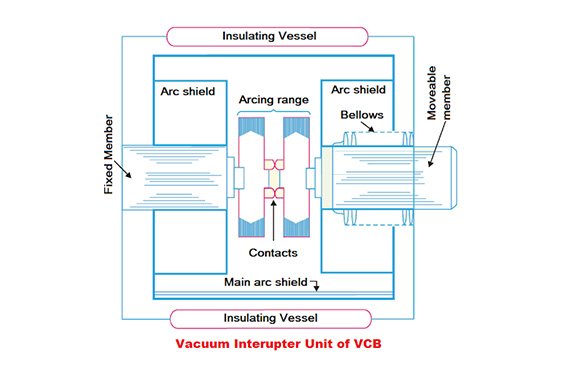
Various Types of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Classification by Voltage Level
- Medium Voltage VCBs: These are typically used in systems with voltage ratings between 1kV and 36kV. They are common in industrial and commercial applications where medium voltage levels are standard.
- High Voltage VCBs: Used in systems above 36kV, these VCBs are essential for high voltage transmission and distribution networks. Their design handles the greater electrical stress found in high voltage applications.
Classification by Application
- Indoor VCBs: Designed for use within buildings, these VCBs are compact and often installed in switchgear panels.
- Outdoor VCBs: These VCBs are built to withstand harsh weather conditions and are used in outdoor substations and power grids.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Pros and Cons of Using Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Advantages
- High Reliability and Longevity: VCBs have fewer moving parts and a sealed vacuum interrupter, which leads to a longer operational life.
- Minimal Maintenance Requirements: Due to their robust design and the vacuum’s efficiency in arc extinction, VCBs require less frequent maintenance compared to other circuit breakers.
- Environmental Benefits: VCBs do not use oil or SF6 gas, making them environmentally friendly and reducing the risk of hazardous emissions.
Disadvantages
- Higher Initial Cost: The advanced technology and materials used in VCBs make them more expensive initially compared to other types of circuit breakers.
- Voltage Limitations: While VCBs are excellent for medium and some high voltage applications, they may not be suitable for the highest voltage levels used in certain power grids.
Applications of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Common Applications of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Industrial Applications
In factories and manufacturing plants, VCBs are essential for protecting machinery and electrical infrastructure. Their reliability ensures continuous operations and reduces downtime due to electrical faults.
Utility and Grid Applications
VCBs are integral to power distribution networks and substations. They provide the necessary protection for transformers and other critical components, ensuring stable and safe power delivery.
Commercial and Residential Use
In buildings and complexes, VCBs safeguard electrical systems from overloads and short circuits. Their compact size and low maintenance needs make them ideal for such applications.
Installation and Maintenance of Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Installing and Maintaining Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Installation Process
Proper installation of VCBs involves several steps:
- Site Preparation: Ensuring the location is suitable and meets safety standards.
- Mounting: Securing the VCB in place, whether it’s in a switchgear panel or an outdoor substation.
- Connection: Connecting the VCB to the electrical circuit with proper wiring and insulation.
- Testing: Conducting initial tests to verify correct installation and operation.
Routine Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures the longevity and reliability of VCBs:
- Scheduled Inspections: Periodic checks of the vacuum interrupter, contacts, and operating mechanism.
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting: Addressing issues such as contact wear, mechanical alignment, and ensuring the vacuum integrity.
Comparison with Other Types of Circuit Breakers
Vacuum Circuit Breakers vs. Other Circuit Breakers
VCBs vs. Air Circuit Breakers
Air circuit breakers use air to extinguish the arc, which is less efficient than a vacuum. VCBs offer superior performance in arc quenching, making them more reliable in medium and high-voltage applications.
VCBs vs. SF6 Circuit Breakers
SF6 circuit breakers use sulfur hexafluoride gas, which is effective but has environmental concerns due to its greenhouse gas properties. VCBs, on the other hand, have no such environmental impact, making them a greener choice.
VCBs vs. Oil Circuit Breakers
Oil circuit breakers use oil for arc extinction, posing fire and maintenance risks. VCBs eliminate these risks, providing a safer and more maintenance-friendly solution.
Future Trends in Vacuum Circuit Breaker Technology
Innovations and Future Trends in Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Advances in Material Science
Improvements in contact materials and vacuum interrupter design enhance the performance and durability of VCBs. These advancements make them more suitable for higher voltage applications.
Smart Vacuum Circuit Breakers
The integration of VCBs with smart grids and the Internet of Things (IoT) is a growing trend. Smart VCBs offer remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and improved operational efficiency.
Market Trends
The demand for VCBs is rising due to their reliability and environmental benefits. Emerging markets, particularly in Asia and Africa, are seeing increased adoption of VCB technology in their power infrastructure.
FAQs about Vacuum Circuit Breakers
Frequently Asked Questions
How do vacuum circuit breakers ensure safety?
VCBs ensure safety by quickly and efficiently extinguishing arcs, preventing electrical fires and equipment damage. Their sealed design also minimizes the risk of external contamination.
What is the lifespan of a typical vacuum circuit breaker?
The lifespan of a VCB can range from 20 to 30 years, depending on usage and maintenance. Regular inspections and timely maintenance can extend this lifespan.
Can VCBs be used in renewable energy systems?
Yes, VCBs are suitable for renewable energy systems. They provide reliable protection for wind and solar power installations, which often require high-quality, durable circuit breakers.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Vacuum circuit breakers are indispensable in modern electrical systems due to their reliability, safety, and environmental benefits. Understanding their working principles, advantages, and applications helps in making informed decisions about their use in various settings. As technology advances, VCBs will continue to evolve, offering even greater efficiency and integration with smart grid technologies.
References
References and Further Reading
For more information on vacuum circuit breakers and related technologies, consider exploring the following resources:
This comprehensive article covers all aspects of vacuum circuit breakers, providing valuable insights and detailed information for readers. By incorporating internal and external links, it ensures readers have access to further resources and related topics.