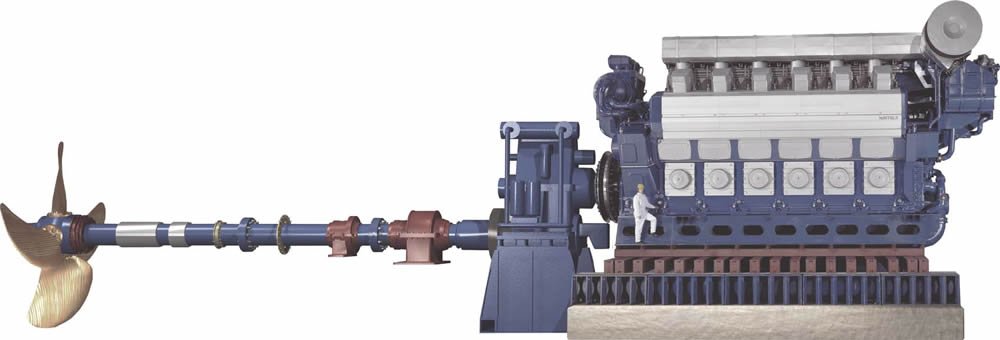
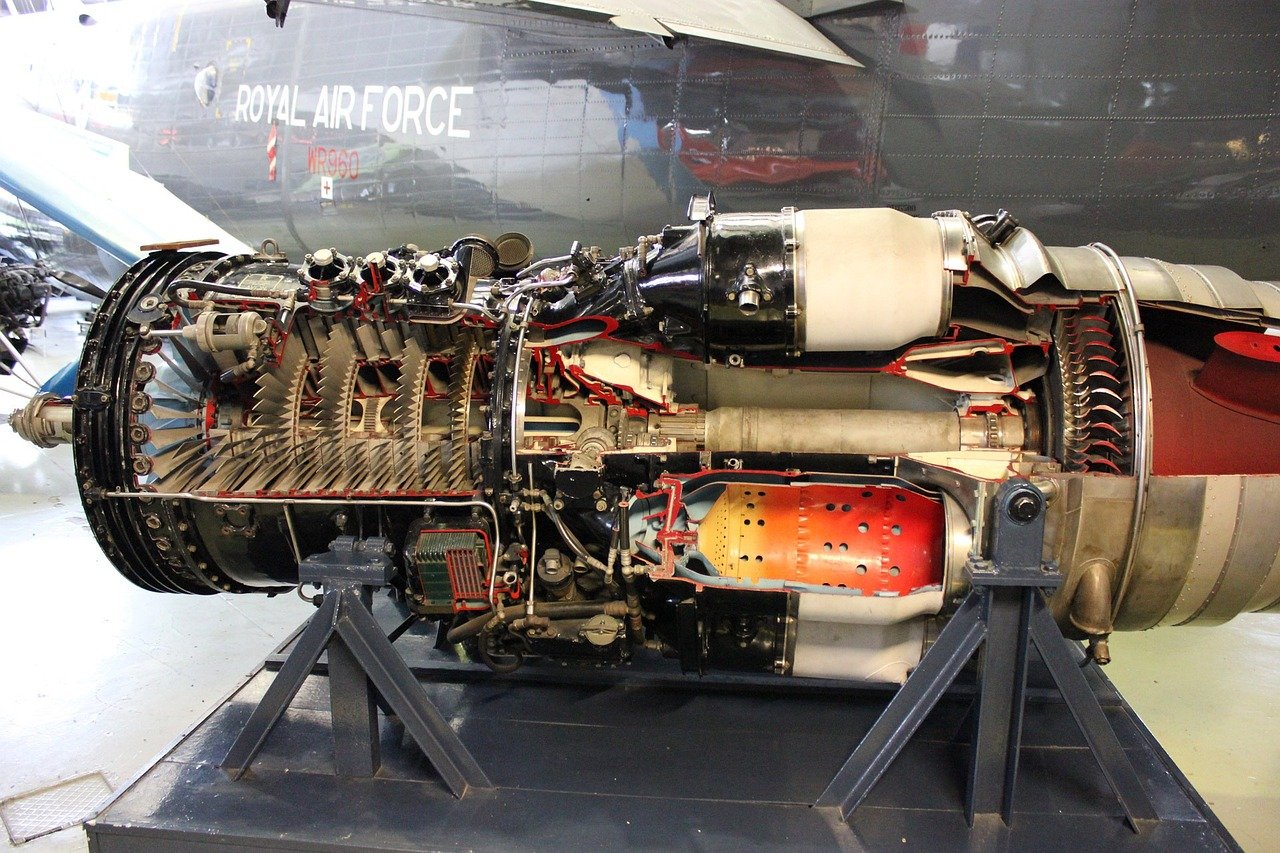
Introduction: Power plants are essential for generating electricity and meeting the energy demands of modern society. One of the key components of a power plant is the engine, which converts energy into mechanical power that can be used to generate electricity. There are various types of engines used in power plants, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. In this blog post, we will explore some of the most common types of engines found in power plants and discuss their functions and applications.
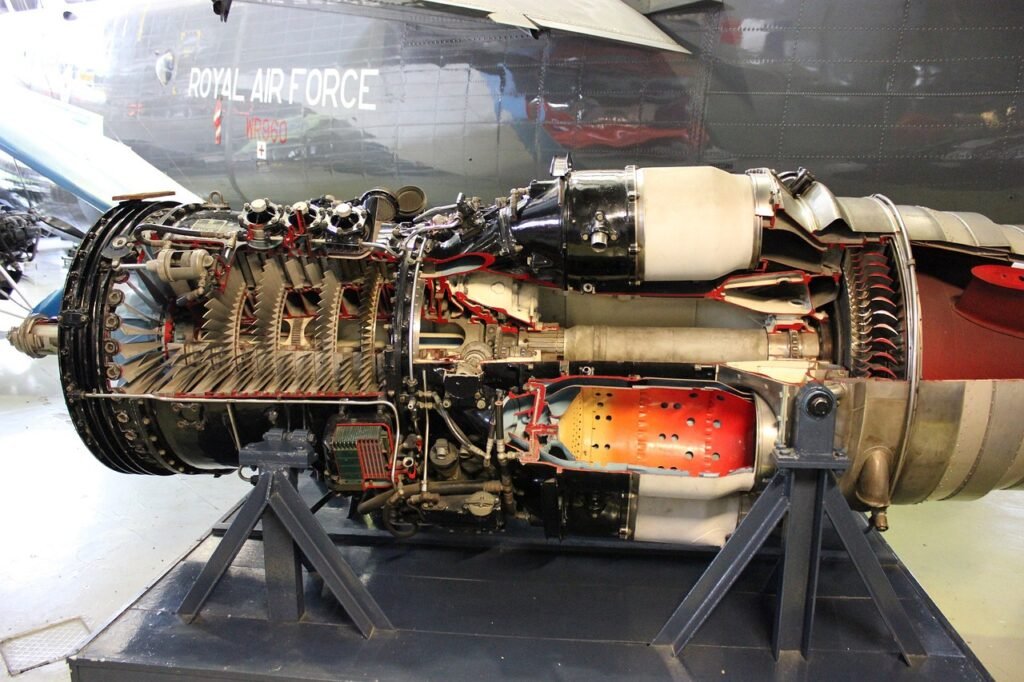
Gas Turbine Engines: Gas turbine engines are widely used in power plants due to their high efficiency and reliability. These engines operate by burning fuel in a combustion chamber to generate hot gases, which then drive a turbine to produce mechanical power. Gas turbine engines are known for their quick start-up times and ability to operate at high temperatures, making them ideal for peaking power plants that need to quickly respond to changes in demand.
Steam Turbine Engines: Steam turbine engines are another common type of engine found in power plants, particularly in coal-fired and nuclear power plants. These engines use steam produced by boiling water to drive a turbine and generate mechanical power. Steam turbine engines are known for their high efficiency and ability to generate large amounts of power, making them well-suited for baseload power plants that need to operate continuously.
Diesel Engines: Diesel engines are often used in small-scale power plants or as backup generators in case of emergencies. These engines operate by compressing air and fuel in a combustion chamber to generate power. Diesel engines are known for their reliability and durability, making them a popular choice for remote locations or areas with unreliable power grids.
Combined cycle engines: They are a hybrid technology that combines gas turbine engines with steam turbine engines to achieve higher efficiency levels. In a combined cycle power plant, the hot exhaust gases from a gas turbine are used to produce steam, which then drives a steam turbine to generate additional power. Combined cycle engines are known for their excellent fuel efficiency and low emissions, making them an environmentally friendly option for power generation.
Conclusion: In conclusion, power plants rely on a variety of engines to generate electricity and meet the energy needs of society. Gas turbine engines, steam turbine engines, diesel engines, and combined cycle engines each play a unique role in power generation, offering different advantages and applications. By understanding the different types of engines used in power plants, we can appreciate the complexity and ingenuity of the technology that powers our modern world.