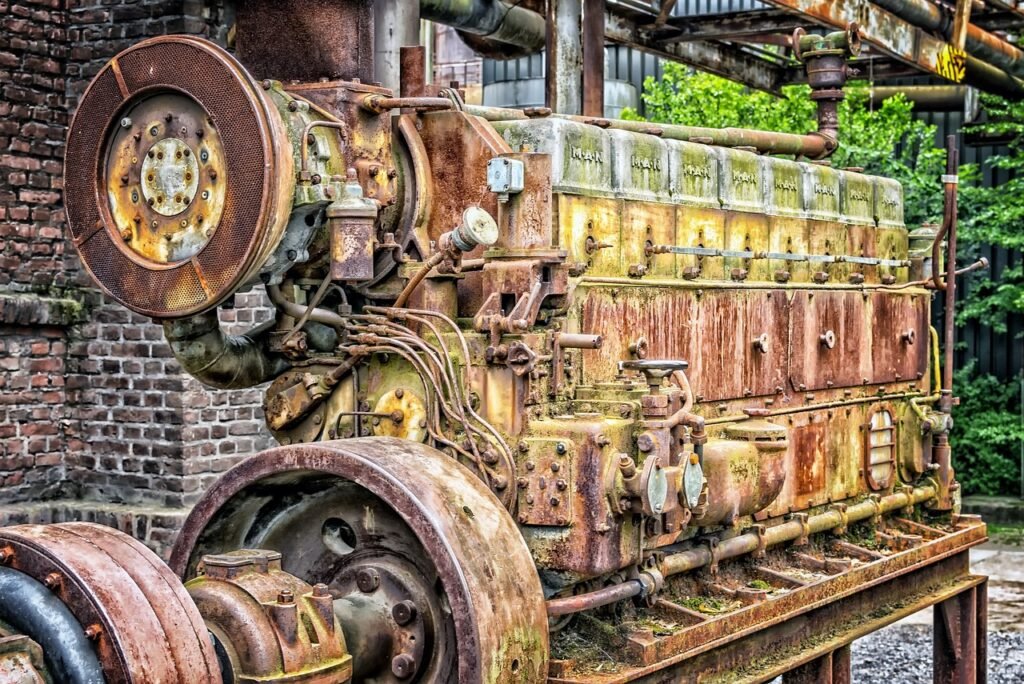
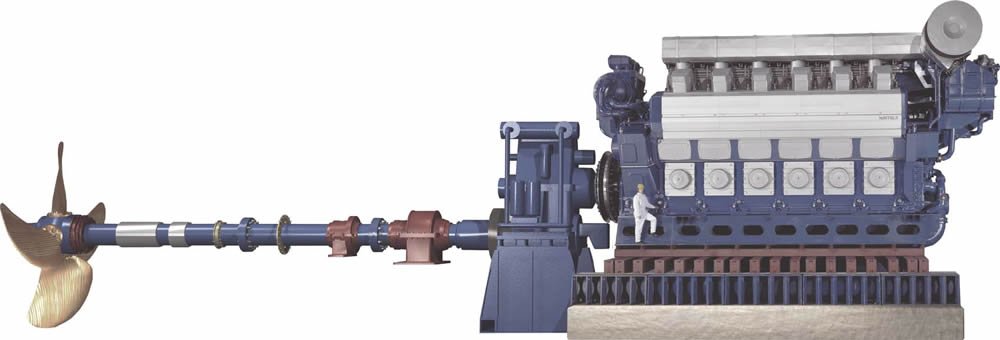
The diesel generator is a type of power supply with a simple work principle, which is rather reliable and effective. The way this equipment works is that it converts the chemical energy of diesel fuel into mechanical. It occurs due to the series of combustion processes and results in the rotation of the internal parts of the generator that allow the electricity. The mechanism is widely used in different industries as it can provide power even in the most distant places or in emergency cases. Thus, knowing how the diesel generator works is essential for its effective utilization.
The Main Parts of Diesel Generator
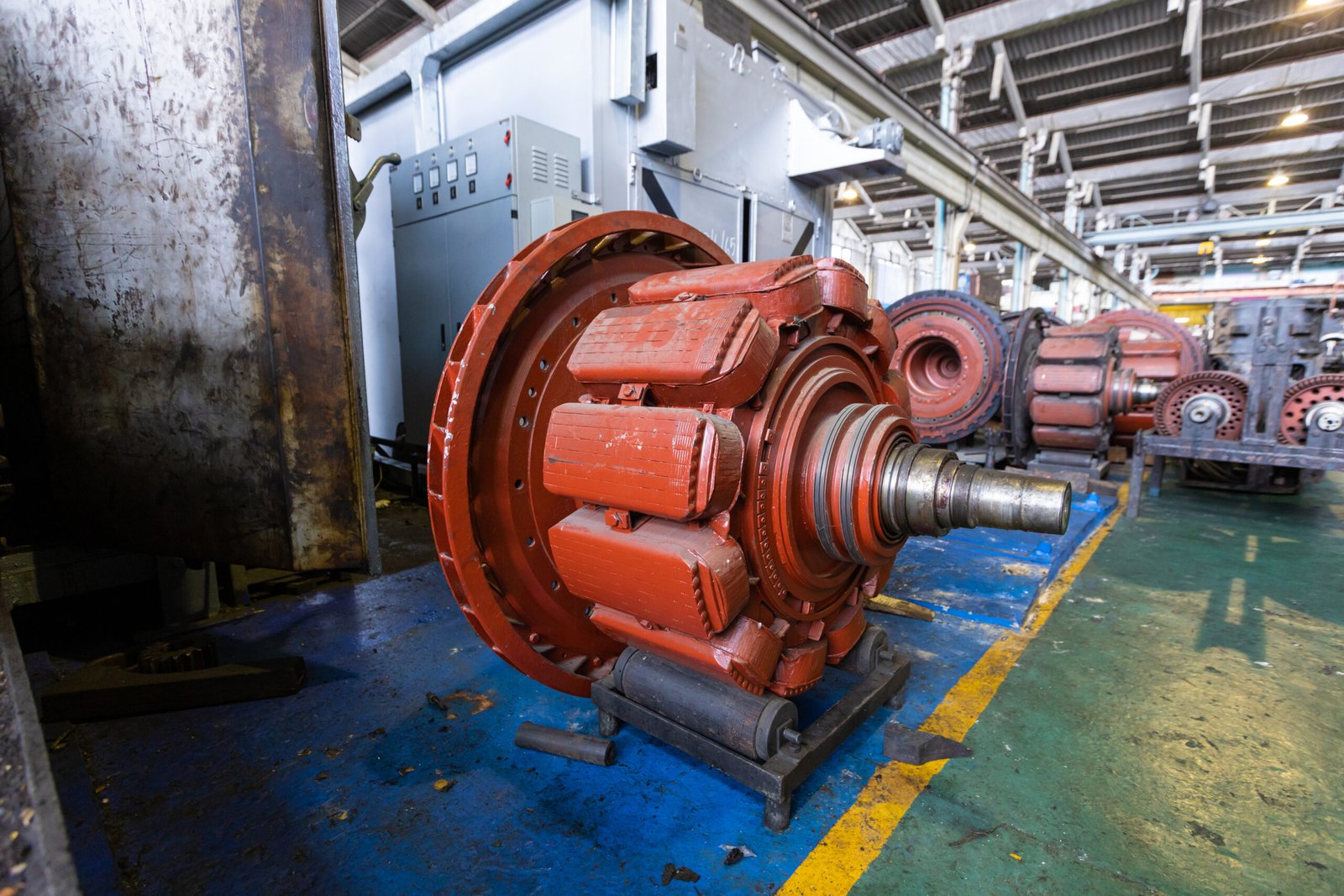
The main parts of a diesel generator constitute crucial components that work together to generate power of electricity efficiently. Thus, a comprehension of their role and functions in this process will facilitate understanding the principal aspects of its working principle. Firstly, the engine is the heart of a diesel generator which converts the chemical energy stored in diesel fuel to mechanical energy through a process of combustion.
Specifically, the engine comprises several vital components, namely the cylinder block, pistons, crankshaft, and fuel injection system. Therefore, the fuel is injected into the combustion chambers of the engine where it mixes with the compressed air and ignites, propelling the pistons down and turning the crankshaft Rodgers, 2018. Secondly, the alternator is another significant part of a generator that transforms the mechanical energy produced by the engine into electricity, consisting of a rotor and stator. In this case, the rotor is driven by the engine forming a rotating magnetic field using generating an electrical current in the form of sine waves in the stator winding.

Main parts of a diesel generator (Reference: https://vitalpower.co.uk/diesel-generators/parts/)
Then, the electric current undergoes a series of several processes converting it into usable electricity. Thirdly, due to the process of power generation diesel generators produce a high amount of heat which needs to be dissipated in order to prevent the overheating of the engine. In this case, the cooling system, including the radiator and cooling fan, assists the maintenance of gases at the appropriate operating temperatures. Consequently, the coolant circulates through the engine absorbing radiated heat from its components and passing through the radiator where it gets cooled down.
Other significant parts of the generator are the fuel system and exhaust system responsible for diesel supply to the engine and expulsion of exhaust gases from it respectively. Specifically, the fuel system comprises the fuel tank, fuel lines, fuel filters, and fuel injectors where filtration of the fuel is crucial owing to prevention of the contaminants from entering the engine.
Finally, the exhaust system includes components of the exhaust manifold, muffler, and exhaust pipe where gases are expelled through the manifold into the turbocharger and then to air via the muffler. Overall, the main parts of a diesel generator act in unity to produce electric power from diesel fuel within the system efficiently. Many of these components have a well-defined function, but it is important to acknowledge them and their operation in order to understand the working principle of a diesel generator.
Diesel Generator Working Principle
To better appreciate the function of this critical equipment, it is important to predetermine the working principle of a diesel generator. It is evident that these machines are becoming increasingly popular and have already become the primary sources of backup power. The knowledge of their working principle will be helpful to operations and maintenance staff because only the reasonable utilization and care of the installed equipment can prolong its life and increase efficiency. This essay will focus on the Diesel Generator Working Principle, meaning that the operation of a diesel generator will be examined thoroughly.
All diesel generators work based on the process of energy conversion. In this case, a diesel engine uses diesel fuel and converts it into electricity. The main components of the diesel generator are the diesel engine, alternator, fuel system, cooling system, and exhaust system.
In the beginning, the diesel engine burns diesel fuel within the combustion chamber. The result of the process is high-temperature, high-pressure gases that power the pistons of the engine. The alternator is also called the generator head and it comprises the rotor and the stator. Functionally, the mechanical energy developed by the diesel engine is moved to the alternator through a connected shaft. The shaft is turning the rotor, and in the presence of a magnetic field of the stator, the rotor is spinning to induce an electric current in the stator windings. In addition, the fuel system, which comprises the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel injector, and fuel filter, burns the diesel fuel in the combustion chamber.
In other words, the fuel pump powers the engine and produces the overall heat in the combustion chamber. Following the considerations about the operation, it is important to mention the significance of the cooling system. It comprises the radiator, coolant, water pump, and thermostat and its main function is to cool the engine. The process involves the removal of heat from the engine by the cooling system. The last part of the process to consider is the exhaust system.
It is important to expel the combustion by-products produced. Some diesel generators can be equipped with a muffler for the reduction of noise. The overall operation of a diesel generator includes fuel burning in the combustion chamber with the development of high-pressure gases, which cool the engine and power the mechanical energy to the alternator for electricity production.
The diesel generator is a backup power supply system that uses a diesel engine to generate electric current. It achieves this by converting the chemical energy in the diesel fuel to mechanical energy with an internal combustion engine, then converting this mechanical energy over an alternator into electrical energy.
Advantages of Diesel Generators:
Reliability: Diesel generators are renowned for their reliability and durability. They can run continuously for prolonged periods without overheating or breaking down, making them ideal for critical applications such as hospitals and data centers.
Fuel Efficiency: Diesel generators are much more efficient than gasoline generators because diesel fuel has a higher energy density. This means that less fuel is needed and the time between refueling increases – an advantage in locations where there isn’t much fuel around for example.
Low Maintenance: Diesel engines are rugged and do not require precise and delicate maintenance like some other engine types. This means lower maintenance costs and a longer life for the generator as a whole.
Longevity: Diesel generators have a longer life than other kinds of generators and prove cost-effective over the long term for backup power.
Disadvantages of Diesel Generators:
Initial Cost: The cost of a diesel generator is more than that of a gasoline generator or other types of power systems. This can be an obstacle, particularly for individuals or businesses on tight budgets.
Noise and Pollution: Diesel generators are loud and generate more exhaust pollution than other types of generators. This can be an issue in residential areas or environmentally sensitive locations.
Maintenance Requirements: While diesel generators require less maintenance than some other engine types, they still need regular service and care to ensure long life and good performance.
Size and Weight: Diesel generators are usually larger and heavier than other kinds of generators, making them less portable and more difficult to transport.
In conclusion, diesel generators offer many advantages including reliability, fuel efficiency, low maintenance, and a long life span. But they also have certain disadvantages like the high up-front costs, noise and pollution concerns, maintenance requirements, and size /weight problems. Understanding all these factors is crucial when deciding if a diesel generator is right for specific power needs.