Comparing Circuit Breakers and Fuses: An Understanding
Safety is critical when it comes to electrical systems. Although they work in different ways, fuses and circuit breakers are both intended to safeguard electrical circuits against overloads and short circuits. Knowing the distinctions between fuses and circuit breakers can enable you to choose the right security solution for your residence or place of company. We shall thoroughly compare and contrast fuses and circuit breakers in this essay.

Circuit Breaker:
– An electrical device known as a circuit breaker is made to automatically cut off power to a circuit upon sensing an overload or short circuit.
– Circuit breakers can be reset after they trip; they are usually located on an electrical panel in a house or place of business.
Circuit breakers come in a variety of forms, such as thermal, magnetic, and thermal-magnetic, and they are all made to trip in reaction to particular kinds of electrical failures.
– Circuit breakers have the benefit of being reversible, although they are more costly than fuses.
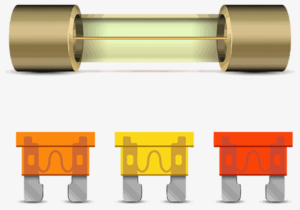
Fuse
– When it senses an overload or short circuit, a fuse is a basic, one-time use electrical device that melts and breaks the circuit.
– Fuses need to be changed when they blow; they are normally placed in a fuse box or electrical panel.
– Fuses are available in various sizes and varieties, such as tiny circuit breakers, glass tube fuses, and cartridge fuses.
– Fuses need to be replaced after tripping, but they are less expensive than circuit breakers.
In contrast:
1. Process:
Circuit breakers stop the flow of electricity by detecting overloads and short circuits through a mechanism.
Fuses work by melting a narrow strip of metal when an excessive amount of electricity passes through it.
2. Restarting
– Circuit breakers allow for fast circuit restoration by being reset when they trip.
– It takes more time and effort to repair fuses once they blow, necessitating replacement.
3. Price:
– The original and replacement costs of circuit breakers are higher than those of fuses.
– Fuses need to be replaced more frequently than circuit breakers, although they are less expensive.
4. Security
– Because circuit breakers can be reset and don’t involve handling live electrical components, they are seen to be safer than fuses.
Fuses can expose users to live electrical currents and must be replaced when they blow.
5. Durability:
– Circuit breakers require less frequent replacement and have a longer lifespan than fuses.
– Fuses need to be changed every time they blow because of their shortened lifespan.
In conclusion, the crucial job of guarding electrical circuits against overloads and short circuits is performed by both circuit breakers and fuses. Cost, convenience, and safety are some of the considerations that influence which option is best. While fuses are less expensive but need to be changed more frequently, circuit breakers have the added advantage of being resettable. The choice between a fuse and a circuit breaker ultimately comes down to your personal preferences and demands.
Learn more about power engineering
For Website design: Click here