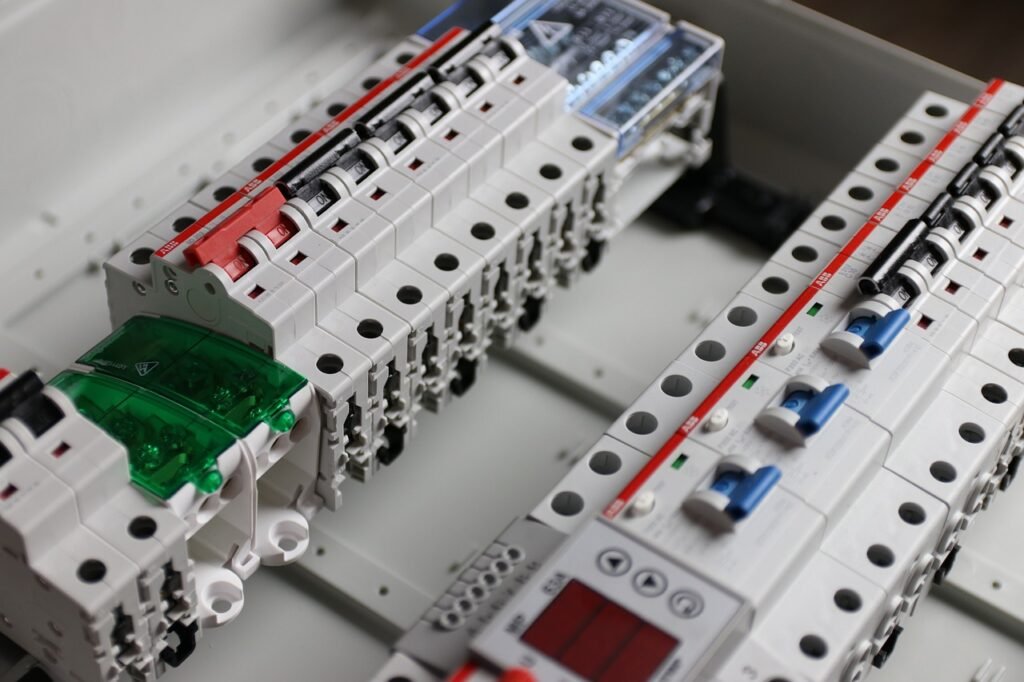
In my childhood days, I used to see cut-out breakers in my house. When there was an overflow of current in the wire, the wire tended to heat up and burn, saving the other appliances in the house. Whenever that happened, my father used to cut a piece of wire and reconnect the inner cores of the wire to the breaker. Though that was a hectic thing to do, it remains a good memory with my father. Days have gone by now, and there are many types of circuit breakers (CB) that can be used in households. In modern houses, many use MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers), while others use RCCBs (Residual Current Circuit Breakers).
Though these are all good, some factors make one better than the other.
RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker):

Purpose: RCCBs are primarily designed to protect against electric shock caused by earth faults or leakage currents. They detect the imbalance in current between the live and neutral conductors, which could occur when current leaks to earth due to a fault or when a person comes into contact with a live conductor.
Protection: RCCBs provide additional safety by quickly disconnecting the circuit when they detect such leakage currents, thus preventing electric shock.
Usage: RCCBs are commonly used in areas where electrical equipment or appliances are at risk of causing electric shock, such as bathrooms, kitchens, outdoor sockets, and areas with wet conditions.
Consideration: While RCCBs offer excellent protection against electric shock, they do not protect against overloads or short circuits. Therefore, they are often used in conjunction with MCBs for comprehensive protection.
MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker):

Purpose: MCBs are primarily designed to protect against overloads and short circuits in electrical circuits. They trip when the current flowing through the circuit exceeds its rated capacity or when a short circuit occurs.
Protection: MCBs protect electrical circuits and appliances from damage due to excessive current, preventing overheating, fire hazards, and damage to connected devices.
Usage: MCBs are used throughout residential and commercial electrical systems to protect individual circuits, such as lighting circuits, power sockets, and appliances.
Consideration: While MCBs provide effective protection against overloads and short circuits, they do not protect against earth faults or leakage currents. Therefore, they are often combined with RCCBs in electrical distribution boards to provide comprehensive protection against various types of faults.